Welcome to the world of innovative pharmaceutical development! In a remarkable breakthrough, scientists at the University of Bath have harnessed the power of nature to create a groundbreaking tool that promises to transform the way we develop pharmaceutical treatments. Inspired by the intricate mechanisms found in nature, this tool opens up new possibilities for sustainable and cost-effective drug development. Join me as we delve into the details of this fascinating discovery and explore its potential impact on the pharmaceutical industry and beyond.
Exploring the Potential of Peptides in Pharmaceutical Development
Unleashing the power of peptides as a game-changer in the pharmaceutical industry.
Traditional small molecules have long been the go-to for pharmaceutical treatments. However, scientists are now turning their attention to peptides, small proteins that hold immense potential in blocking disease-related protein interactions. Despite their advantages, peptides and proteins pose challenges due to their unstable structures and difficulty in penetrating cells.
But fear not! Inspired by nature, researchers at the University of Bath have developed a groundbreaking technique to overcome these hurdles. By creating 'cyclic' proteins and peptides, they have achieved enhanced stability and improved cell penetration. This innovative approach holds great promise for revolutionizing drug development.
Nature's Blueprint: Harnessing the Power of Cyclic Proteins
Unlocking the secrets of cyclic proteins and their potential in pharmaceutical treatments.
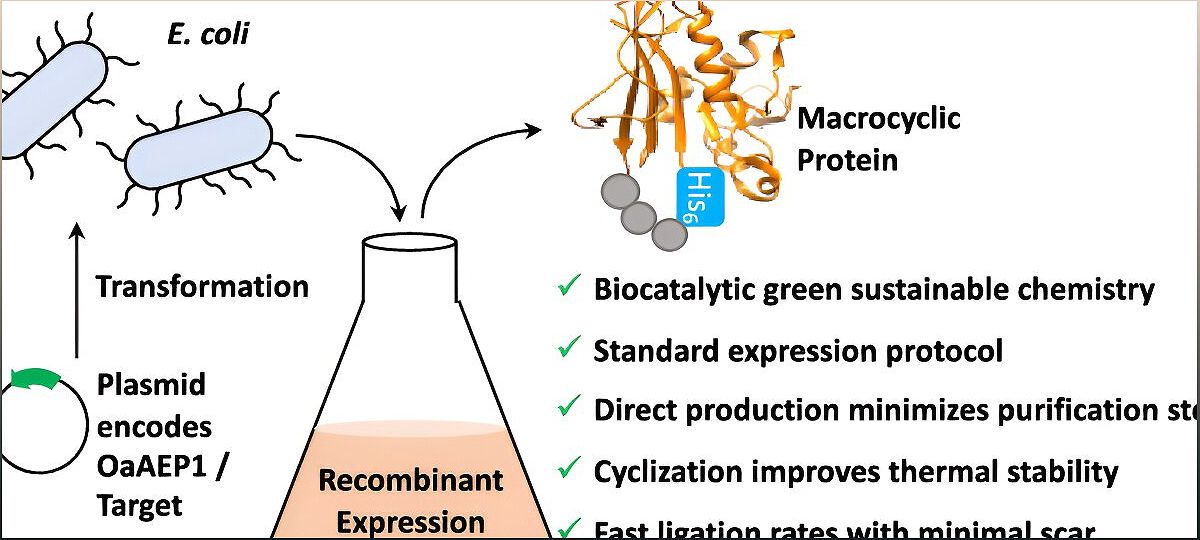
Nature has always been a master architect, and cyclic proteins are a testament to its brilliance. These proteins, with their joined loose ends, exhibit remarkable stability and enhanced functionality. Drawing inspiration from a tropical flower called Oldenlandia affinis, the researchers at the University of Bath have harnessed the power of an enzyme called OaAEP1 to create cyclic proteins.
By transferring this modified enzyme into bacterial cells, they have unlocked a sustainable and efficient method of mass-producing cyclic proteins. This breakthrough not only accelerates drug development but also paves the way for applications in various industries, including biotechnology and bioenergy production.
From Theory to Reality: Demonstrating the Effectiveness
Putting the technique to the test: showcasing the effectiveness of cyclic proteins.
The true test of any scientific breakthrough lies in its practical application. The researchers at the University of Bath have successfully demonstrated the effectiveness of their technique by applying it to a protein called DHFR. This protein, known for its sensitivity to temperature changes, showcased increased resistance while maintaining its normal function.
These promising results not only validate the potential of cyclic proteins but also open up new avenues for developing temperature-resistant drugs. With this technique, the possibilities for pharmaceutical advancements are endless.
A Sustainable Future: Benefits Beyond Pharmaceuticals
Unveiling the wide-ranging benefits of cyclic proteins in various industries.
The impact of cyclic proteins extends far beyond the realm of pharmaceuticals. Their enhanced stability and cell penetration properties make them invaluable in industries such as food, detergent, and biotechnology. Imagine the possibilities of creating temperature-resistant enzymes for industrial processes or developing eco-friendly bioenergy production methods.
This groundbreaking tool developed by the researchers at the University of Bath has the potential to revolutionize multiple industries, making them more sustainable, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly.